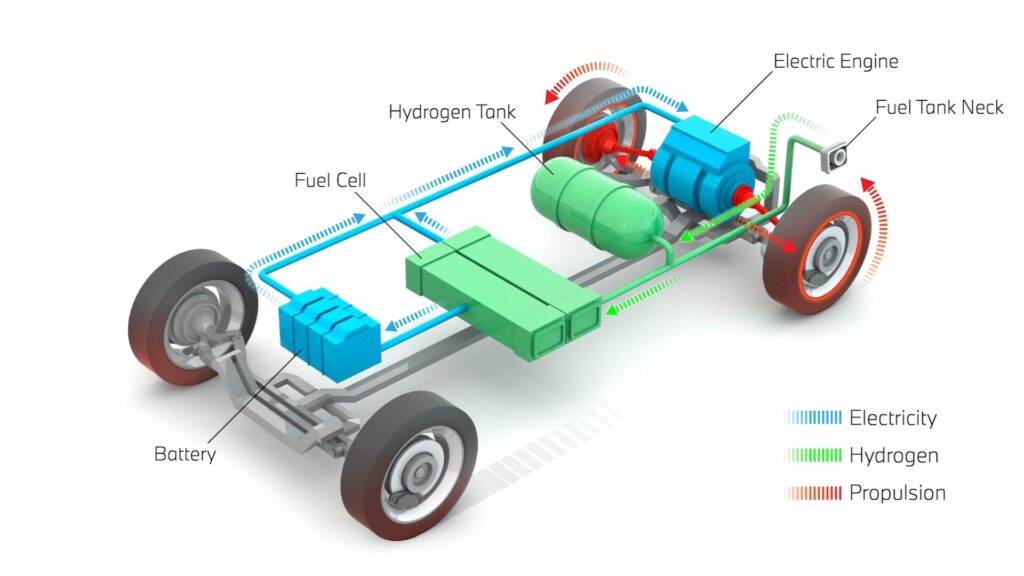
How Does Electric Vehicle Powertrain Technology Function? Have you ever wondered about the inner workings of electric vehicles? As EVs gain popularity, understanding their powertrain technology becomes increasingly relevant. Unlike traditional combustion engines, electric vehicles utilize a sophisticated system of batteries, motors, and controllers to propel themselves forward. This innovative approach to transportation offers numerous benefits, from reduced emissions to improved energy efficiency. In this article, you’ll discover the core components that make electric vehicles function and gain insight into how this technology is revolutionizing the automotive industry. Join us as we explore the fascinating world of EV powertrains and their impact on the future of mobility.
What are the Main Components of an Electric Vehicle Powertrain?
Understanding how EV works requires familiarity with its key components. The electric vehicle powertrain consists of several essential parts that work together to propel the vehicle efficiently.
Battery Pack
At the heart of an EV is its battery pack. This large, rechargeable lithium-ion battery stores electrical energy and powers the entire system. The battery’s capacity determines the vehicle’s range and performance.
Electric Motor
The electric motor converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors provide instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration.
Power Electronics Controller
This component acts as the brain of the EV, managing power flow between the battery and motor. It controls acceleration, regenerative braking, and overall vehicle performance.
Onboard Charger
The onboard charger converts AC power from charging stations into DC power to charge the battery. It’s crucial for replenishing the EV’s energy source. How Does Electric Vehicle Powertrain Technology Function?
Thermal Management System
To maintain optimal performance and longevity, EVs employ sophisticated cooling systems. These regulate the temperature of the battery, motor, and other components.
Understanding these core components helps explain how EV works and why electric vehicles are becoming increasingly popular for their efficiency and environmental benefits.
How Does the Motor Provide Power in an EV?
When considering how does ev work, it’s essential to understand the role of the electric motor. Unlike traditional combustion engines, electric vehicles (EVs) utilize one or more electric motors to convert electrical energy into mechanical power, propelling the vehicle forward.
The Basics of Electric Motors
At the heart of an EV’s powertrain is the electric motor. These motors operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, using the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents to generate rotational force. This process is highly efficient, converting up to 90% of electrical energy into mechanical energy, far surpassing the efficiency of internal combustion engines.
Power Delivery in EVs
One of the key advantages of electric motors is their ability to provide instant torque. This means that when you press the accelerator, the motor responds immediately, delivering power to the wheels without the delay typically associated with gasoline engines. This characteristic contributes to the smooth and responsive driving experience that EVs are known for.
Regenerative Braking
Another unique feature of EV motors is their ability to work in reverse, acting as generators during deceleration. This process, known as regenerative braking, allows the motor to capture kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost as heat in traditional braking systems. The recaptured energy is then stored in the battery, extending the vehicle’s range and improving overall efficiency.
Understanding the Function of the EV Battery Pack
The battery pack is the heart of how an electric vehicle (EV) works, providing the energy needed to power the motor and propel the car forward. Understanding its function is crucial to grasping how EVs operate.
Composition and Design
EV battery packs typically consist of thousands of individual lithium- ion cells, similar to those found in smartphones but much larger. These cells are arranged in modules and connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. The pack’s design prioritizes energy density, thermal management, and safety.
Energy Storage and Delivery
When you plug in your EV to charge, electricity flows into the battery pack, where it’s stored as chemical energy. As you drive, this stored energy is converted back into electricity to power the electric motor. The battery management system (BMS) carefully regulates this process, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. How Does Electric Vehicle Powertrain Technology Function?
Range and Efficiency
The battery pack’s capacity directly influences an EV’s range. Modern EVs can travel 200-400 miles on a single charge, depending on the model. Factors like driving style, terrain, and climate affect how efficiently the battery’s energy is used. Understanding these factors can help you maximize your EV’s range and performance.
By grasping how EV battery packs function, you’ll better appreciate how electric vehicles work and their potential to revolutionize transportation.
How does Charging Work for Electric Vehicles?
Understanding how EV charging works is crucial for potential electric vehicle owners. The process is straightforward, but it’s important to grasp the basics to ensure efficient and safe charging practices.
Charging Basics
At its core, charging an electric vehicle involves connecting it to a power source that replenishes the battery. This process is similar to charging your smartphone, but on a much larger scale. When you plug in your EV, the charger converts AC (alternating current) from the grid into DC (direct current) that the battery can store.
Charging Levels
There are three main levels of EV charging:
- Level 1: This is the slowest method, using a standard 120V household outlet. It’s convenient but can take 8-20 hours for a full charge.
- Level 2: Utilizing a 240V outlet, this method is faster and is commonly found in homes and public charging stations. It can fully charge most EVs in 4-8 hours.
- DC Fast Charging: The fastest option, capable of charging up to 80% of an EV’s battery in 30-60 minutes. These are typically found along highways and in urban areas.
Electric Vehicle Powertrains vs Gasoline Vehicle Powertrains
Core Differences
When considering how EVs work compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, the powertrain is a key differentiator. In a gasoline vehicle, the engine converts fuel into mechanical energy through combustion. This energy is then transferred through a complex transmission system to the wheels. In contrast, an electric vehicle’s powertrain is significantly simpler. How Does Electric Vehicle Powertrain Technology Function?
EV Powertrain Components
The heart of an EV powertrain is the electric motor. Unlike a gas engine with hundreds of moving parts, an electric motor has relatively few. This simplicity contributes to the efficiency of how EVs work. The motor is powered by a large battery pack, typically located in the floor of the vehicle for optimal weight distribution and center of gravity.
Energy Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of EV powertrains is their energy efficiency. While gasoline engines convert only about 20-30% of fuel energy into motion, electric motors can convert over 90% of stored energy into movement. This efficiency is a key factor in understanding how EVs work and why they’re gaining popularity.
Regenerative Braking
Another unique feature of EV powertrains is regenerative braking. When you brake in an EV, the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electricity to recharge the battery. This system further enhances the overall efficiency of electric vehicles, demonstrating another aspect of how EVs work to maximize energy use.
Conclusion
As you’ve seen, electric vehicle powertrains represent a revolutionary shift in automotive technology. By harnessing the power of advanced batteries, efficient electric motors, and sophisticated control systems, EVs offer a cleaner, quieter, and potentially more sustainable transportation solution. While challenges remain in areas like charging infrastructure and battery longevity, ongoing innovations continue to push EV capabilities forward. As this technology matures, you can expect to see even greater advances in range, performance, and affordability. Whether you’re considering an EV purchase or simply staying informed about emerging automotive trends, understanding the core functions of electric powertrains provides valuable insight into the future of transportation.